Bridging the Gap: How AI Could Transform Doctor-Patient Communications
In the ever-evolving landscape of healthcare, seamless communication between doctors and patients is crucial. Yet, this vital component often encounters obstacles, ranging from time delays to misinterpretation of medical jargon. However, the emergence of artificial intelligence (AI) offers unprecedented opportunities to bridge these gaps. This post delves into how AI is set to transform digital communications between doctors and patients.
To unpack this, we will explore two innovative approaches for enhancing communication with patients. The first is more forward-looking - facilitating direct chat capabilities with patients. Imagine someone reaching out with an urgent health concern, be it an illness, rash, or injury. While some scenarios may necessitate physical consultations, many can be effectively managed through immediate virtual guidance, with a provision for follow-up if needed.
The second approach addresses a more conventional communication channel: messages within the patient portal. Currently, clinicians are overwhelmed by the volume of such interactions. This often leads to delayed responses, compromised response quality, and increasing clinician burnout. We will examine how AI can significantly address these issues, fostering a more efficient and satisfying communication experience for both patients and healthcare providers.
These examples will showcase how AI not only promises to bridge the communication gap in healthcare but also paves the way for a more connected, responsive, and patient-centered healthcare ecosystem.
How AI could Enable Chatting with the Patient
AI-powered chat systems represent a significant leap in managing patient inquiries efficiently. By leveraging large language models (LLMs), these chatbots can understand and respond to a wide range of patient questions in real-time, from inquiries about symptoms and medication side effects to guidance on aftercare and lifestyle adjustments. This immediate interaction not only expedites the resolution of common queries but also significantly reduces the workload on healthcare staff, allowing them to focus on more complex cases. Moreover, these AI chat systems can be made available 24/7, ensuring patients have access to reliable information whenever they need it, thereby improving patient satisfaction and engagement with their healthcare.
A key question is whether patients can trust this information? In a recent study, a team of investigators set out to learn whether one could tell the difference between answers from experts or a chatbot, and how good those answers were. To do so they used an online eye care forum where patients could ask detailed questions and receive answers from physicians affiliated with the American Academy of Ophthalmology.
The team assembled a panel of 8 board-certified ophthalmologists who independently reviewed the forum questions and were randomly presented either a human-written or AI-generated answer for each question in a masked fashion. Let’s see what they found:
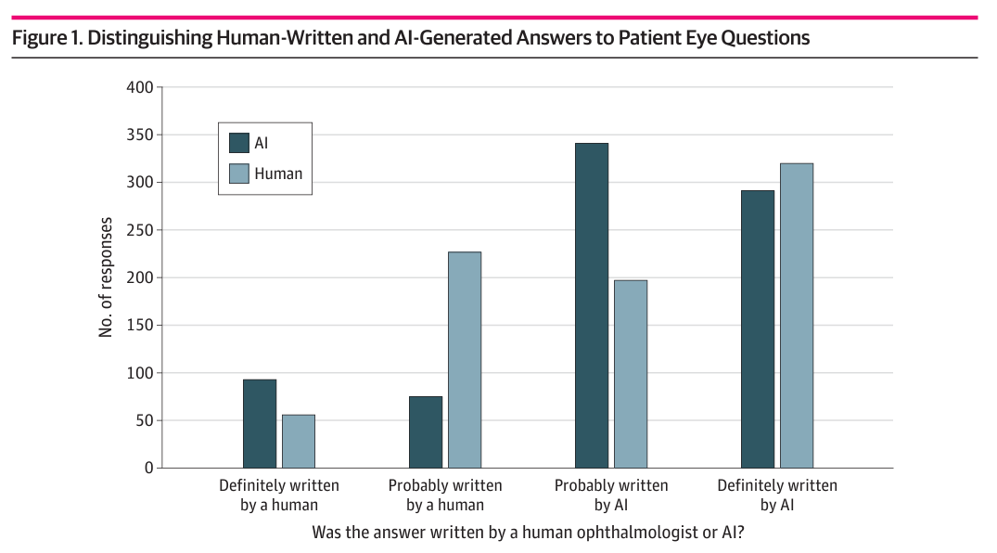
1. Was the answer written by a human ophthalmologist or AI?
When asked if questions were either definitely written by a human or definitely written by AI, it’s basically a toss up. The expert panel had trouble telling the difference.
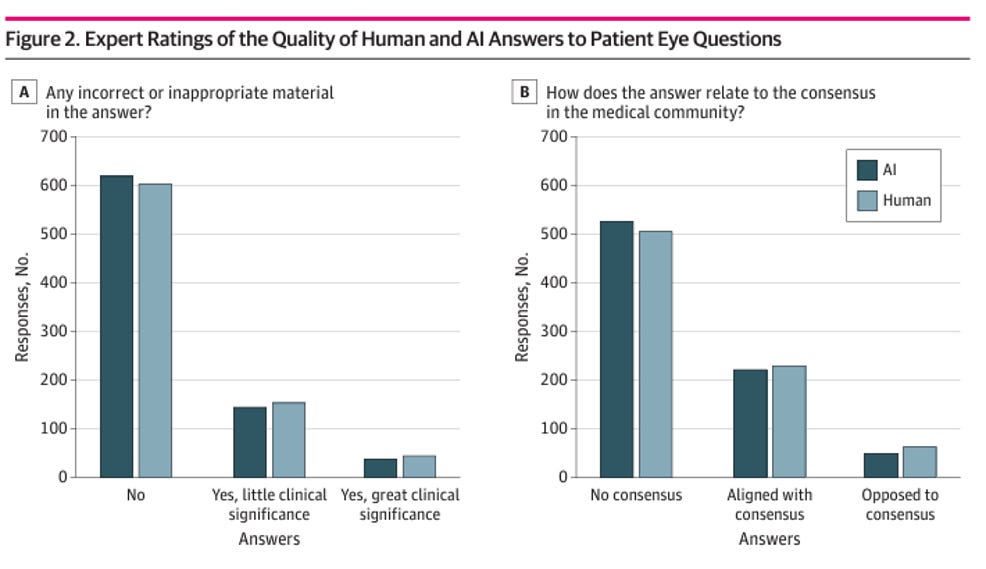
2. Rating the quality of the answers
As you can see, pretty much every question was rated similarly, indicating it was difficult to say that one had better or worse quality than the other.
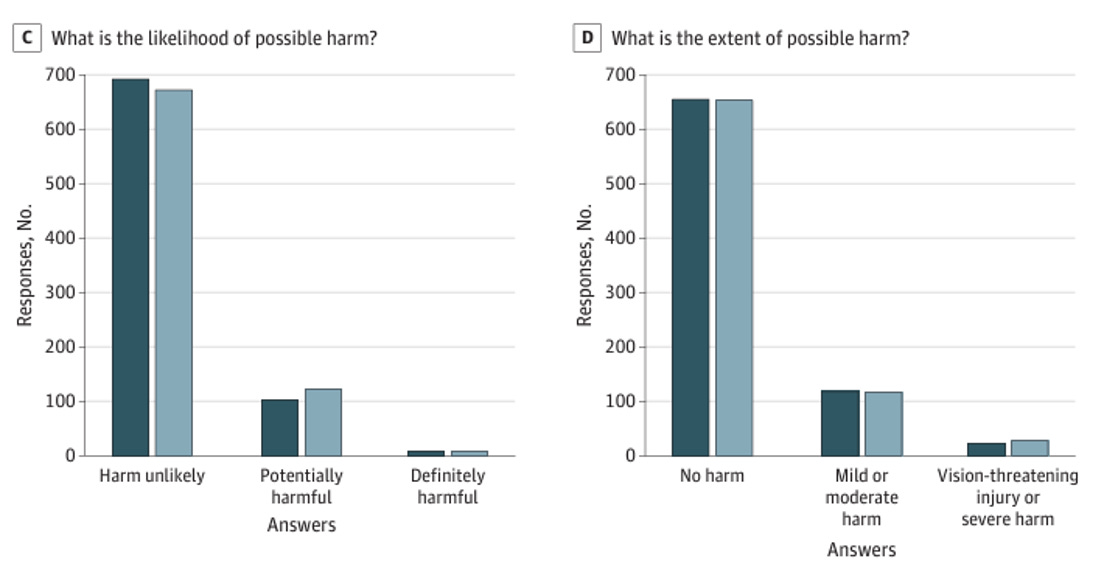
3. Could the answers cause harm?
As you can see, about 10-15% of responses were marked as potentially harmful. But interestingly, the findings were similar whether a human or AI wrote the responses. In sum, these findings all support the potential role that AI could play in helping quickly respond to patient medical questions.
Responding to Patient Portal Messages
It’s no secret that clinicians struggle to keep up with their inbox of patient inquiries. These are often sent through a patient portal. Since clinicians spend most of their time caring for patients, they have very little time (if any) allocated to respond to messages from patients. Many clinicians will try to do this after work and before going to bed - a practice that has become known as “pajama time.” One physician describes his experience during the pandemic in an essay published in JAMA called Death by Patient Portal.
How could AI help?
The use of AI to draft responses in patient portals is another transformative application. AI algorithms could analyze patient messages and generate draft responses based on the patient's medical history, the nature of their inquiry, and standard care protocols. This assists healthcare providers in managing their correspondence more efficiently, ensuring timely and accurate communication with their patients. Furthermore, these AI-generated drafts can be customized or reviewed by healthcare professionals before sending, maintaining the personal touch and accuracy of the information provided. This blend of AI efficiency with professional oversight enhances the quality of communication, making it more personalized and responsive to patient needs.
Epic, one of the largest electronic health record vendors in the US, has described how they are working on building tools to help clinicians more efficiently respond to patient portal messages with AI. Here’s an article from a pilot conducted at UC San Diego. They noted a couple of interesting points:
AI responses appear to be most helpful for primary care physicians, who are perhaps getting more general questions. They think this is because the chatbots are trained using information available on the internet. For the questions that specialists receive, the LLMs likely have less data to learn from.
Generative AI is generating longer responses than physicians would typically send on their own, which could be more thoroughly addressing the inquiry
An addendum is added to every message that explains the response was automatically generated and then reviewed and edited by the physician who signed it. This improves transparency which is a key tenet towards building trust
Frequently Asked Questions
How could AI chat systems ensure patient privacy and confidentiality, especially with sensitive medical information?
AI chat systems designed for healthcare applications should be developed with a strong emphasis on data security and privacy, adhering to regulations such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States. These systems should employ encryption, secure data storage, and access controls to ensure that patient information remains confidential and is only accessible by authorized personnel. Additionally, ongoing monitoring and audits help to maintain the integrity and security of patient data.
How can AI handle the nuance and complexity of medical language, especially when interpreting patient symptoms or queries?
AI-powered systems, particularly those utilizing large language models (LLMs), will need to be trained on vast amounts of medical literature, clinical case studies, and patient interactions, enabling them to grasp the nuances of medical terminology and patient expressions. Natural language processing (NLP) techniques would allow these AI systems to interpret the context of patient queries accurately, differentiate between similar-sounding symptoms with distinct causes, and provide responses that are relevant and understandable to patients. Continuous learning from interactions and feedback further refines their ability to handle complex medical language.
Can AI in healthcare communication adapt to changes in medical knowledge and treatment guidelines?
AI systems are inherently designed to be adaptable and can be regularly updated with the latest medical research, treatment protocols, and guidelines. Through machine learning algorithms, these systems could incorporate new information, ensuring that the advice and responses provided to patients and healthcare professionals are current. In some implementations, AI systems are integrated with medical databases and journals that automatically update, allowing the AI to learn from the most recent and relevant data. This adaptability ensures that AI-powered communication tools remain a valuable and reliable resource in healthcare. It will be important that these updates have proper oversight and are reviewed by clinicians.